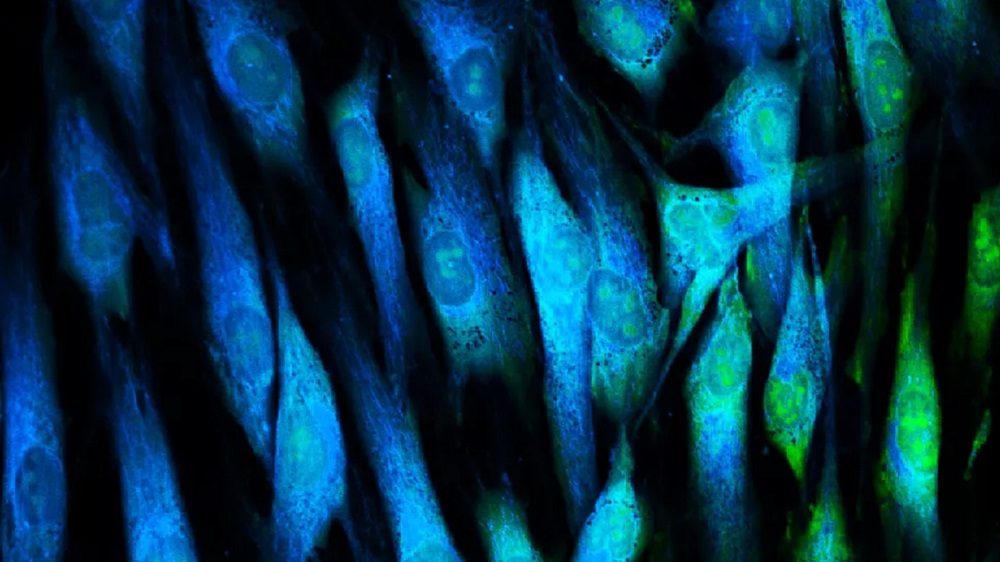
Scientists May Have Discovered The Secret To Eternal Youth

It has been women’s and men’s fantasies for generations and now, ccording to experts, it is possible to reverse the aging process in human skin. Cambridge researchers have reprogrammed the skin cells of individuals aged 38 and 53 to make them appear up to 30 years younger.
The procedure reverses the aging process more effectively than earlier reprogramming techniques without causing cell damage. Researchers claim that they can even partially recover lost functionality in aged cells.
The researchers assert that while the research is still in its infancy, the discoveries might someday revolutionize regenerative medicine, especially if they can be duplicated in different cell types and bodily tissues.
De-aging has become quite popular in the last few years
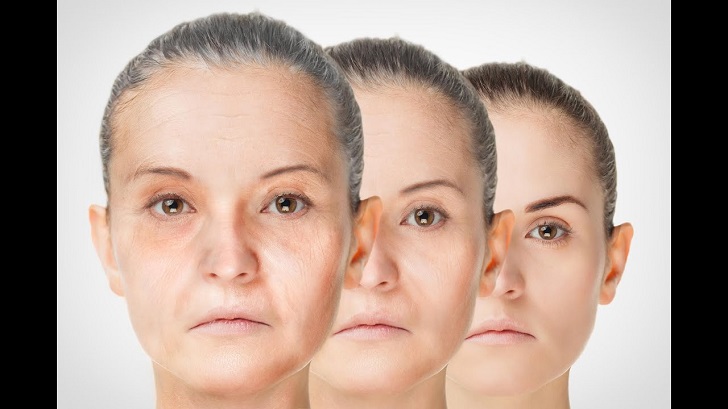

Youtube/ Mxresdefault | Researchers have developed a method that turns back the biological clock of skin cells thirty years
Scientists have reprogrammed multiple mice, rat, and human cell types during the past decade in an effort to reverse cellular aging. But never before have so many years been removed from a cell’s age while preserving its kind and function.
The technique, developed by Diljeet Gill, a postdoctoral candidate at the Babraham Institute in Cambridge, and his colleagues, was published on April 8 in the journal eLife(opens in a new tab) under the name “maturation phase transient reprogramming.”
The researchers employed this approach to fibroblasts (a common kind of skin cell) from three middle-aged donors (average age: 50) and compared them to cells from younger donors (average age: 20 to 22). The researchers discovered that the middle-aged cells were chemically and genetically comparable to the younger ones. Further investigation revealed that the approach altered genes associated with age-related disorders like Alzheimer’s disease and cataracts.
Gill and his colleagues also examined the fibroblasts’ activity to discover if they might behave like younger skin cells. When they injured a layer of cells, they discovered that the rejuvenated cells moved quickly to fill the void, just as younger cells do when healing wounds.
Turning back time
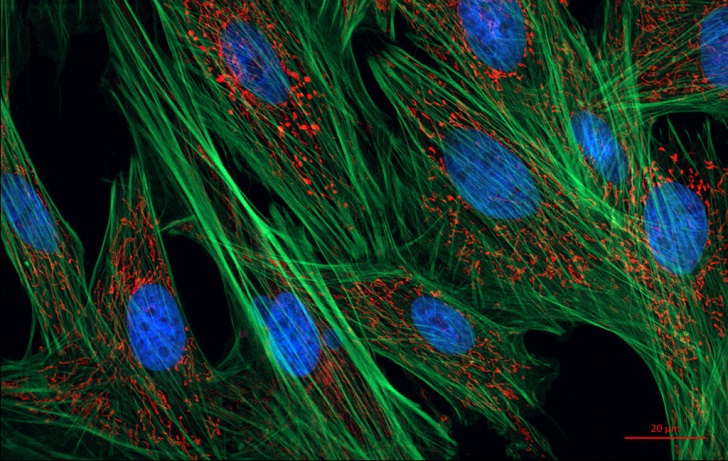
Time/ Huid | Exposure to certain molecules can reverse the aging of skin cells while preserving their function.
Based on the Nobel Prize-winning procedure used to create stem cells, the new method circumvents the challenge of completely deleting cell identity by stopping reprogramming partway through the process. This enabled scientists to establish the optimal balance between reprogramming cells to make them biologically younger and regaining their specialized cell function.
Shinya Yamanaka was the first scientist to transform normal cells with a specified purpose into stem cells with the capacity to grow into any cell type 2007. Using four critical molecules known as the Yamanaka factors, stem cell reprogramming takes around 50 days. The new technique, termed “maturation phase transient reprogramming,” exposes cells to Yamanaka factors for only thirteen days. At this stage, age-related alterations are eliminated, and the cells momentarily lose their identity.
The partially reprogrammed skin cells were allowed to develop under normal settings to determine if their original function had reappeared. Analysis of the genome revealed that reprogrammed cells had recovered fibroblast-like characteristics, and collagen synthesis in the reprogrammed cells verified this.
Results of the study

Healthline/ Pinterest | The sun is one of the biggest contributors to early skin aging
The study’s findings were published in the life sciences journal eLife. The article said cosmetics are not the sole use for this new treatment. According to Babraham experts, this cellular treatment might be utilized to treat several medical ailments. As fresher cells create more collagen, the therapy might aid in the restoration of brittle bones, the healing of strained ligaments and tendons, the healing of skin lesions, and the structural repair of damaged tissue.
Cellular de-aging may potentially improve other age-related disorders. Alzheimer’s disease is linked to the APBA2 gene, revitalized by the MPTR epigenetic treatment. In addition, the MAF gene, which can cause cataracts, has shown improvement in response to the anti-aging medication.
More in Anti-Aging
-
`
Should I Visit a Chiropractor? The Tell-Tale Signs
If you’re wrestling with persistent discomfort in areas like your neck, back, or shoulders, you’re not alone. Many Americans are intimately...
July 19, 2024 -
`
Chad Smith and Will Ferrell Drum-Off – A Night of Comedy and Music
The year was 2014. The late-night talk show landscape was abuzz with a brewing battle unlike any other. It wasn’t a...
July 8, 2024 -
`
Can Coughing Cause Back Pain?
Back pain is a common complaint among many individuals, but did you know that a simple action like coughing can exacerbate...
July 5, 2024 -
`
How to Overcome Imposter Syndrome?
Imposter Syndrome is a familiar term many recognize as a psychological state where individuals doubt their accomplishments, fearing that others will...
June 27, 2024 -
`
Which Peptides Are Best for Anti-Aging?
For those seeking to combat the signs of aging and maintain a youthful appearance, the world of skincare can feel overwhelming....
June 18, 2024 -
`
Celebrities with Celiac Disease – Inspirational Stories and Struggles
Celiac disease is a serious condition, and even the rich and famous aren’t immune. Many celebrities have been open about their...
June 10, 2024 -
`
How to Fix Poor Sleep Hygiene for Better Rest
Sleep is a fundamental human need, as crucial for our well-being as a healthy diet and regular exercise. Yet, many people...
June 6, 2024 -
`
5 Easy & Effective Ways of Coping With Depression
Depression is more than just feeling sad or having a bad day. It is a pervasive mental health condition that affects...
May 30, 2024 -
`
Top 10 Practical 60th Birthday Ideas For Everyone
Turning 60 is a milestone worth celebrating! Whether you are planning your own bash or organizing a celebration for a loved...
May 24, 2024













You must be logged in to post a comment Login